- Arthritis is a common condition affecting millions of people in the US, and it has various types, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Age, genetics, gender, injury, and lifestyle choices are some factors that increase the risk of developing arthritis.
- Treatment options include massage, physical therapy, medication, and surgery.
- It is possible to manage arthritis with the right approach and treatment plan.
- Talk to your doctor to determine the best course of action.
Arthritis is a common disease that tends to affect people in their older ages. Almost 58 million adults in the United States are diagnosed with some form of arthritis, which makes up 23% of the adult population, according to the CDC. It is a broad term referring to more than 100 rheumatic diseases and conditions that affect the joints and surrounding tissues.
Arthritis can be challenging, affecting mobility and daily activities and causing severe pain and inflammation. But with modern medicine and treatments, it is possible to alleviate the symptoms of arthritis and improve the quality of life. It is essential to know about arthritis, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options to understand its impact on daily life better.
Types of Arthritis
There are two most common types of arthritis – Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease that primarily affects the joints and is caused due to the wearing down of the cartilage that cushions the joint’s bones.
On the other hand, Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily targets the synovial lining of the joints and can potentially affect the whole body. It can also destroy the joint surfaces and surrounding cartilage, causing severe pain, inflammation, and stiffness.
Causes of Arthritis
There are various reasons for this disease. Here’s what you need to know about it:
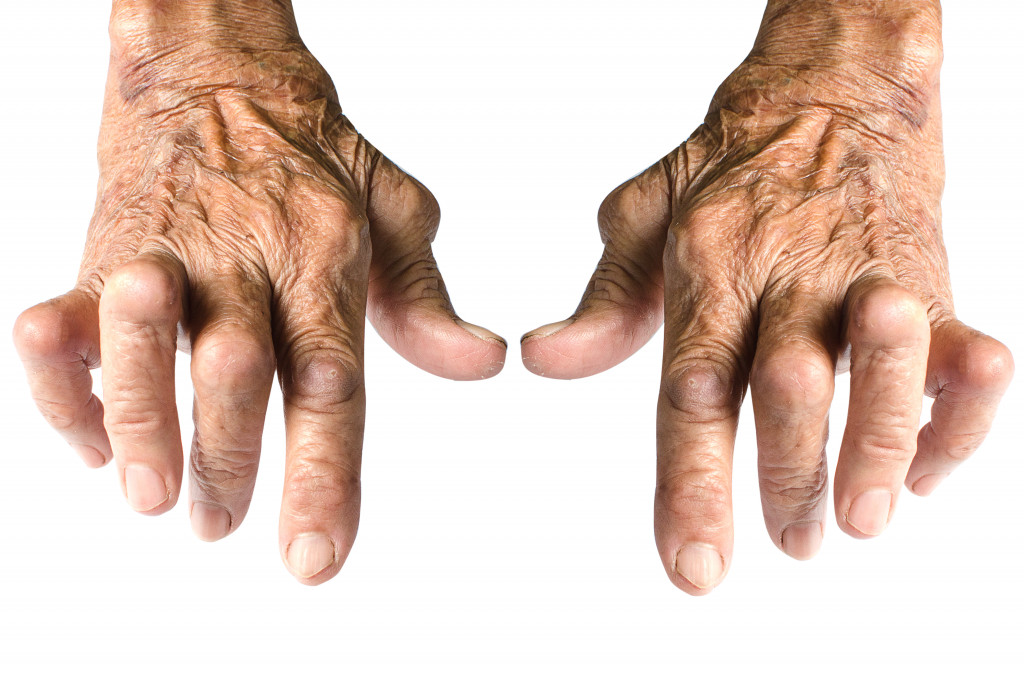
Age
One of the primary risk factors for arthritis is age. As you age, your joints tend to wear out and become less flexible, leading to an increased risk for arthritis. Arthritis is most common in individuals aged 65 years and older. However, it is essential to note that while age is a contributing factor, arthritis can also affect younger individuals, especially those with a family history of the condition.
Genetics
Genetics plays an essential role in developing arthritis, and people with a family history may be at increased risk. Several genes are associated with the development of arthritis, and researchers are still uncovering more about genetic risk factors. However, it is essential to note that just because you have a family history of arthritis does not mean you are guaranteed to develop the condition.
Gender
Studies have shown that women are more likely than men to develop arthritis, particularly rheumatoid arthritis. Women are three times more likely than men to develop this condition. The reason is unclear, but researchers suspect hormonal factors and biological differences between men and women contribute to this. Women should, therefore, be vigilant and take necessary precautions to reduce their risk of developing arthritis.
Injury
Joint injuries, especially those that cause damage to the joint cartilage and ligaments, increase the risk of developing arthritis over time. Injuries, like fractures or tears, do not necessarily lead to arthritis, but repeated injuries can accumulate and cause long-term damage to the joints, increasing the risk of arthritis.
Lifestyle Choices
Several lifestyle choices can increase the risk of developing arthritis. These include a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and being overweight or obese. Lack of exercise can lead to weak muscles, causing joint stress and arthritis. Smoking has been associated with rheumatoid arthritis and can worsen symptoms. Being overweight or obese puts excess stress on the joints, causing them to wear out more quickly, thus increasing the risk of arthritis.
Treatment
There are various treatments for this disease. Here are some of them:
Massage
Blood flow is crucial for treating arthritis. A good massage therapy can ensure the affected areas receive increased blood flow and reduce inflammation. Massage can also help relax tense muscles, reducing joint stress and pain.
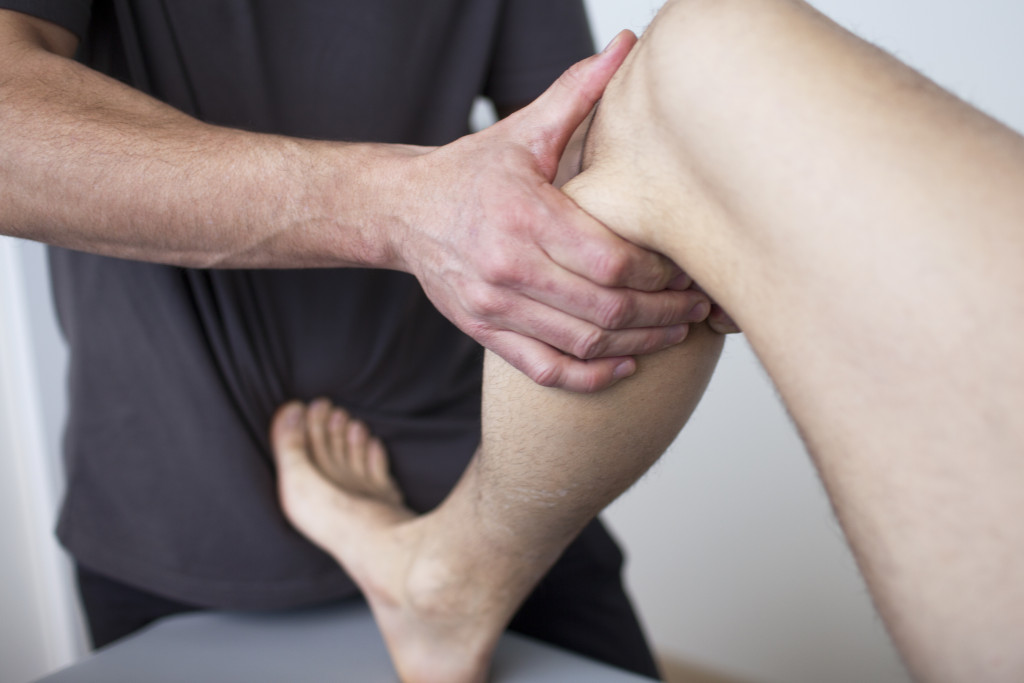
Physical Therapy
Regular exercise is essential for relieving arthritis pain. Physical therapy helps to build strength in the affected joints and improve their flexibility, reducing the risk of further damage. Physical therapists will work with patients to develop an exercise program tailored to them.
Medication
Doctors may also prescribe medication to relieve arthritis symptoms like short-term inflammation or long-term relief from chronic pain syndromes. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling in the joints, but they often come with side effects like nausea, headaches, and stomach irritation. If NSAIDs are not an option, other medications like corticosteroids and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to fix damaged joints or to replace them entirely with artificial ones. Surgery is the last resort for treating arthritis as it carries risks of complications. However, if the condition fails to respond to conservative treatments, surgery can relieve severe pain and disability.
Living with arthritis is often tricky, but there are ways to manage and reduce the symptoms. Understanding the causes and treatments of the condition can help you make informed decisions about your care plan and improve your quality of life. Talk to your doctor about diagnosis, treatment, and management options. With the right approach, it is possible to lead a healthy and active lifestyle despite arthritis.

