- Gum disease is an infection of the gums caused by bacteria buildup in the mouth.
- Common causes of gum disease include tooth loss, poor oral hygiene, genetics, and smoking.
- Symptoms of gum disease can range from red, swollen, and bleeding gums to receding gums and loose teeth.
- Treatments for gum disease may include professional cleanings, improved oral hygiene, or gum surgery.
- To help prevent gum disease, practice good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing daily and visiting a dentist regularly. Avoid smoking and maintain a balanced diet.
Periodontitis, commonly called gum disease, is a prevalent condition that impacts millions of individuals across the globe. It occurs when bacteria in the mouth build up and cause inflammation and damage to the gums and supporting tissues of the teeth. Left untreated can lead to tooth loss and other serious health complications. This blog post will discuss gum disease’s causes, symptoms, and treatments, so you can be better informed and take steps to prevent it.
What is Gum Disease
In general, gum disease is an infection of the gums that typically occurs when plaque builds up and causes irritation to the gum tissue. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that accumulates on the surface of teeth over time. If not removed, it can lead to inflammation and weakening of the supportive structures around your teeth, resulting in periodontal disease.
Causes
Most people consider dental problems typical inconveniences that can be fixed through basic oral hygiene or a visit to their dentist. Among the most common oral health concerns is gum disease – an infection of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. Gum disease is a severe condition that can worsen if not identified and treated immediately. Here are the common causes:
Tooth Loss
One of the most common causes of gum disease is tooth loss, often leading to gum tissue loss. Tooth loss enables food particles and bacteria to accumulate in the gum pockets, which eventually causes inflammation. This makes it difficult to clean the gum line thoroughly and can lead to infection if left untreated.
As such, opting for tooth replacement solutions when you experience tooth loss, such as dental implants or bridges is crucial. Doing so will help to prevent the spread of bacteria and the further progression of gum disease.
Poor Oral Health
One of the easiest ways to develop gum disease is by neglecting your oral hygiene. Poor dental care practices allow plaque and tartar to build up, leading to gum disease. Keeping your teeth clean through daily brushing and flossing, as well as regular visits to the dentist, is crucial to gum disease prevention.
Genetics
The risk of gum disease can be higher for people with a family history of the condition. Suppose you have an immediate family member who has had gum disease or has lost their teeth. In that case, it’s essential to be vigilant to maintain a healthy oral hygiene regimen.
Smoking
People who smoke cigarettes or use tobacco products are at a higher risk of developing gum disease. Nicotine restricts the blood flow to the gums, making it harder for them to heal if infected.
Symptoms
Gingivitis, the initial stage of gum disease, manifests as red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, it can advance to periodontitis, which poses a significant threat to teeth and gums, causing severe damage. Common signs of periodontitis encompass gum recession, tooth mobility, halitosis, and the presence of pus around the teeth and gums. If you notice any of these symptoms, you must see a dentist or hygienist immediately.
Treatments
The treatment for gum disease depends on the severity of the condition. Professional cleaning and improved oral hygiene may reverse the damage in mild cases. Gum surgery may be necessary in more advanced topics to repair the damaged tissue and prevent further complications. Your dentist or hygienist can recommend the best treatment plan based on your needs.
Prevention
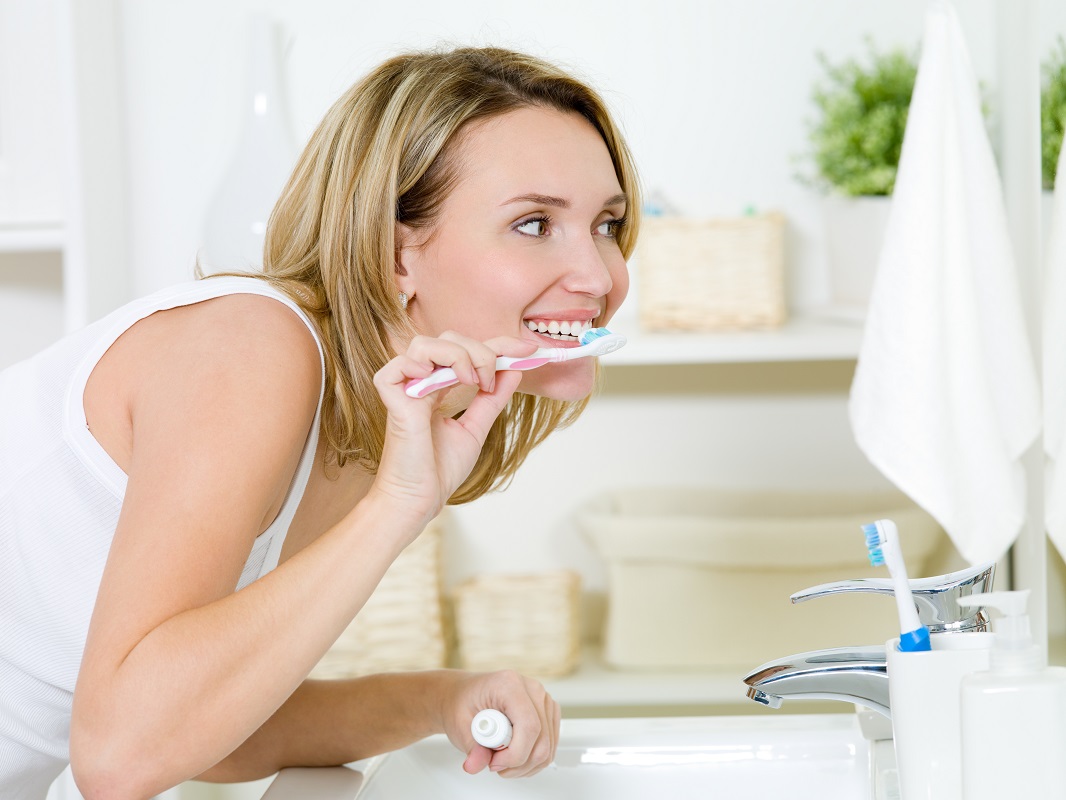

Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is crucial in preventing gum disease. This involves brushing and flossing daily, incorporating an antiseptic mouthwash, and scheduling regular cleanings and check-ups with a dentist or hygienist. You should also avoid smoking and maintain a balanced diet to promote healthy gums and oral health. By following these practices, you can effectively safeguard your oral health and reduce the risk of gum disease.
Final Thoughts
Gum disease is a common condition with severe consequences if left untreated. With the proper knowledge and preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of gum disease and maintain a healthy smile.
Remember to brush and floss daily, see a dental professional regularly, and avoid smoking or other habits that can damage your oral health. By caring for your gums and teeth, you can enjoy a lifetime of healthy smiles and overall well-being.

